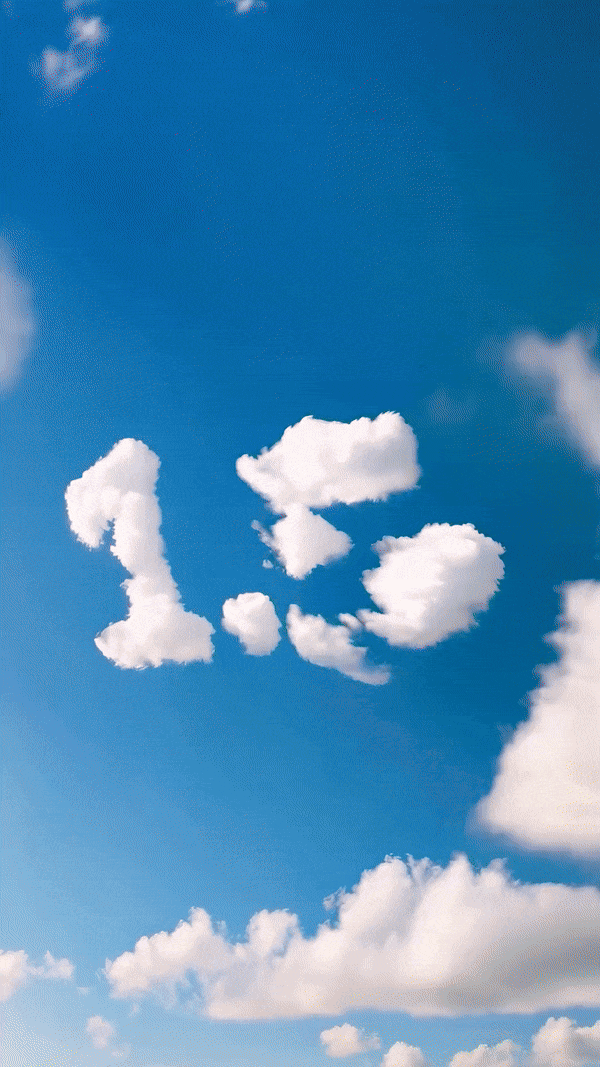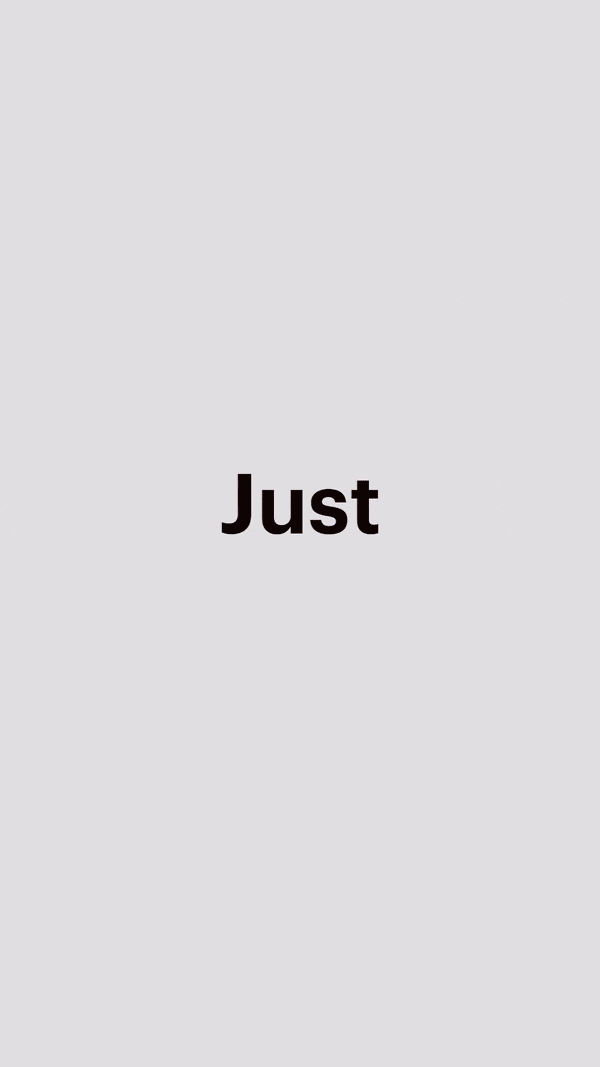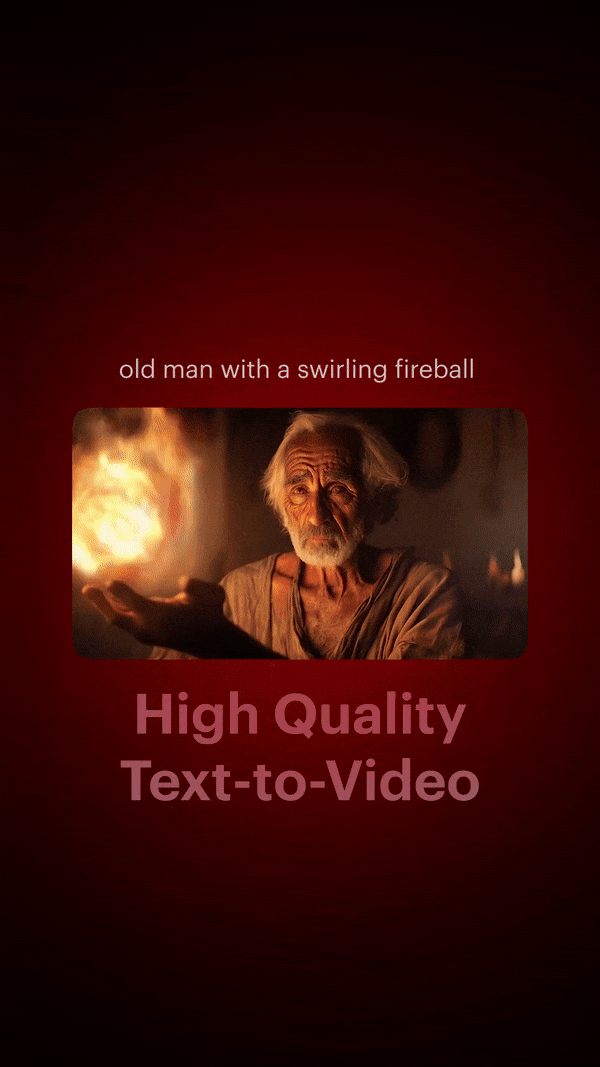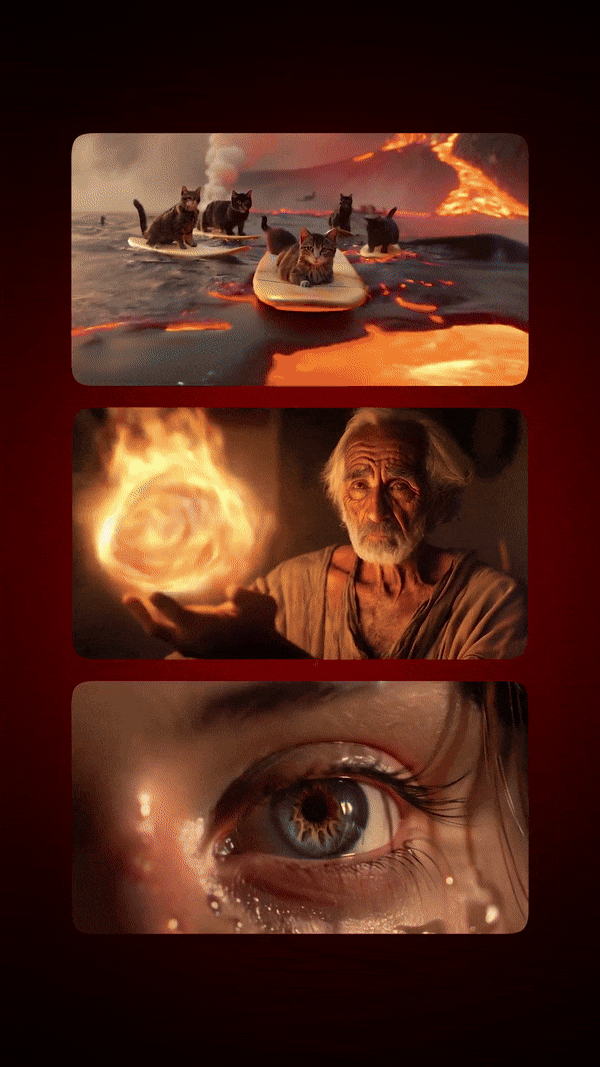🧠 Rent a Brain-Powered Biocomputer for $500 a Month & China's Robots Rip 🤖
What you actually need to know about AI, weekly.
Welcome to this week in AI.
This week, watch a brain-powered biocomputer live, Eric Schmidt reveals Google’s dirty laundry and Chinese companies make iRobot a reality.
Are you ready?
👋 If you’re new here, welcome!
Subscribe to get your AI insights every Thursday (usually).
Rent a Brain-Powered Biocomputer for $500 a Month
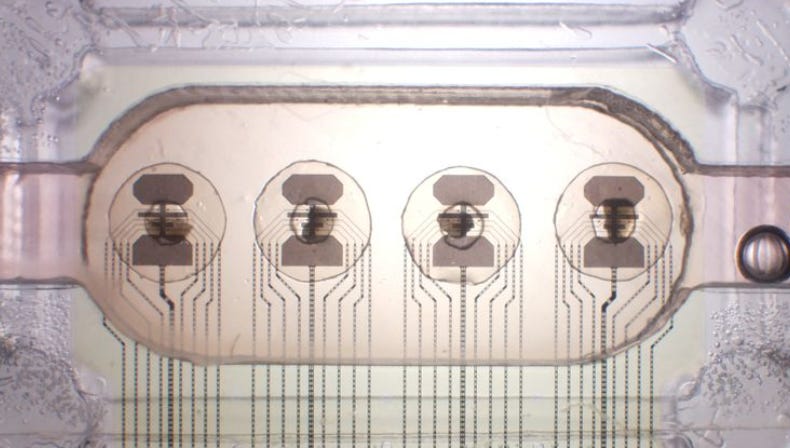
In the quest for more energy-efficient AI, scientists are turning to a novel field: biocomputing.
This emerging technology leverages living cells, such as brain organoids, to create computers that consume significantly less energy than traditional silicon-based hardware.
Companies like FinalSpark are pioneering this approach, offering rentable biocomputer platforms to researchers.
While still in its early stages, biocomputing promise a more sustainable and efficient AI paradigm, with potential applications ranging from advanced AI training to environmental monitoring.
Why it matters
AI's insatiable appetite for energy is a growing concern, and biocomputing offers a potential solution.
By harnessing the power of biology, we could dramatically reduce the environmental impact of AI, enabling its continued growth and development.
Biocomputing also represents a new frontier in technological innovation, blurring the lines between the digital and biological worlds.
This feels like a precursor to Terminator…
Why Google Fumbled AI At The Start
Eric Schmidt's candid insights into the accelerating pace of AI development highlight Google's potential misstep in prioritising work-life balance over aggressive innovation.
Schmidt, who oversaw Google's acquisition of DeepMind and the development of transformative technologies like the Transformer architecture (LLMs), now believes the company may have lost its competitive edge due to a less intense work culture.
He contrasts this with the relentless drive of startups and figures like Elon Musk, emphasising the importance of speed and scale in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
Why it Matters
Schmidt's observations serve as a cautionary tale for established tech giants.
As companies grow, they often become bureaucratic, slowing down decision-making and innovation.
This atrophy can create opportunities for smaller, nimbler competitors to disrupt the market with new technologies.
His comments underscore the potential consequences of complacency, even for industry titans like Google.
📝 A good read by Exponential View
Dream Big With Luma Lab’s New Model
Luma Labs has just upgraded its AI video generation model, Dream Machine, to version 1.5.
This update brings improved realism, motion, and prompt understanding, enhancing the model's ability to generate high-quality video clips from text and images. It's faster too, producing five-second videos in just two minutes.
While it may not be as revolutionary as some previous AI video advancements, it showcases Luma Labs' ability to shipping new features consistently.
Why it Matters
The release of Dream Machine 1.5 is a testament to the relentless pace of AI innovation, with text-to-video capabilities becoming increasingly sophisticated and accessible.
As AI video generation continues to evolve, we can expect to see more realistic and creative content produced with ease, opening up new possibilities for storytelling and communication.
China's Robot Revolution: Humanoid Helpers on the Horizon
Astribot S1
Astribot S1, a humanoid robot, excels at various tasks, from cooking to playing instruments. Its "Design for AI" architecture enables human-like interaction, making it a potential companion for research, commercial, and home settings.
Unitree G1
Unitree G1, a mass-producible humanoid robot, offers impressive agility and versatility at an affordable price of $16,000. Its advanced features include leaping, twisting, obstacle navigation, and fall resistance.
AGIBOT
AGIBOT, a new humanoid robot company, has secured funding and launched a family of robots, including the flagship Yuanzheng A2. The A2 is designed for diverse tasks and aims to compete with Tesla's Optimus.
Why it Matters
Humanoid robots could significantly contribute to addressing various challenges, including the aging population in Western and other advanced economies.
By providing care for older individuals, robots could reduce the burden on healthcare systems and lessen reliance on taxes.
Additionally, robots could generate vast amounts of new training data for AI, as they interact with the world and learn from their experiences.
This would be especially valuable given the near-exhaustion of known written data.
Furthermore, the increased competition in the humanoid robot market, driven by companies like AGIBOT, is likely to lower the price point of these robots, making them more accessible to individuals and businesses.
Elon Musk's prediction of producing over 1 billion robots annually highlights the potential scale of this industry and its transformative impact on society.
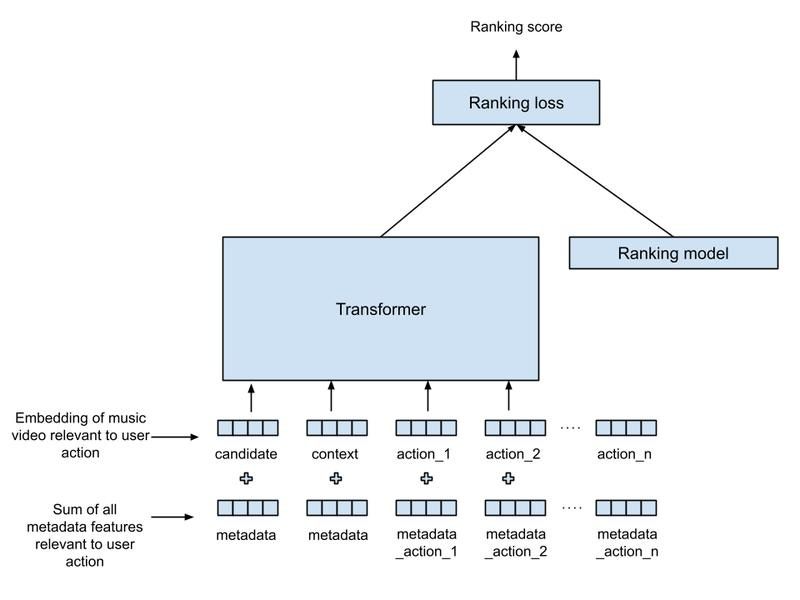
YouTube Music's Transformer-Powered Recommendations
Google's YouTube Music has introduced a novel music recommendation system that leverages Transformer models, commonly used in language processing (like LLMs), to enhance the personalisation of music suggestions.
Unlike traditional methods, this system analyses the sequence and context of user actions like likes, dislikes, and skips, considering factors such as the user's current activity or mood.
By integrating this understanding with existing ranking models, YouTube Music can deliver music recommendations that better align with the user's immediate preferences and context, even if it deviates from their usual listening patterns.
Why it Matters
This innovation directly translates to a more enjoyable and satisfying user experience.
By accurately capturing the nuances of user preferences in real-time, the system reduces skip rates and increases listening time.
This means users are discovering music they truly enjoy, enhancing their overall engagement with the platform.
Furthermore, this development underscores the potential of applying Transformer models beyond traditional language tasks, opening doors for more sophisticated and context-aware recommendation systems across various domains.
Missed the last one?
That’s a Wrap!
If you want to chat about what I wrote, you can reach me through LinkedIn.
If you liked it, give it a share!