Google's New Agentic AI 🤯 Tiny AI Model Outperforms GPT-4o 💥
PLUS: Incredible 4K Video Generation 🎬, OpenAI Updates, and More
👋 Welcome to this week in AI.
🎵 Don’t feel like reading? Listen to two synthetic podcast hosts talk about it instead.
📰 Latest news
Gemini 2.0: Ushering in the Era of Agentic AI
Google has launched Gemini 2.0, an upgraded multimodal AI platform featuring improved performance, expanded multimodality, and integrated tool use.
The experimental Gemini 2.0 Flash model reportedly doubles the speed of prior versions. Multimodal capabilities now include image and audio generation alongside processing.
Critically, Gemini 2.0 integrates external tools like Google Search and code execution, enabling "agentic" behaviours—the ability to plan and execute actions based on user instructions.
Prototypes like Project Astra (universal assistant), Project Mariner (browser task completion), and Jules (coding assistant) demonstrate these agentic capabilities.
Why it matters
The shift towards "agentic" AI with Gemini 2.0 signals a shift in user interaction with AI systems.
Moving beyond simple query response, these systems aim to anticipate needs and complete tasks, offering a more proactive and integrated experience.
Tool integration expands the scope of AI action, potentially bridging information retrieval and execution.
While prototypes are experimental, they give us a glimpse at what’s to come.
📝 Try Gemini 2.0 Flash now (free)
📰 Article by Google on Gemini 2.0
AI-Generated Video: Google's Latest Models Set a New Standard
Google has launched Veo 2, a next-generation video generation model capable of producing 4K videos (720p at launch) with lifelike human movement, cinematic camera control (wide, POV, drone shots), and simulated physics.
Veo 2 has outperformed leading models in human evaluations.
Imagen 3, Google’s upgraded image generation model, now generates more diverse art styles with improved accuracy, detail, and prompt adherence, also achieving state-of-the-art results.
Whisk, a new Google Labs tool, lets users remix images using Imagen 3 and Gemini's visual understanding.
Veo 2 is available via VideoFX with future YouTube Shorts integration, and Imagen 3 is accessible through ImageFX in over 111 countries. Both models use SynthID watermarks.
Why it Matters
Veo 2's release is part of a broader industry trend toward increasingly sophisticated AI-driven video generation.
While Veo 2 demonstrates significant advancements, it's one of several models pushing the boundaries of what's possible in this space.
The increasing accessibility and quality of these tools, including Veo 2, will contribute to a substantial rise in AI-generated video content online.
This proliferation has implications for content creation workflows across various sectors, including marketing, advertising, and entertainment, potentially lowering production barriers and enabling new forms of visual storytelling.
It also raises important questions about content authenticity, copyright, and the potential for misuse.
Google's development of a competitive video generation model, alongside continued advancements in image generation and other AI domains, reinforces its position as a major player in the competitive AI landscape.
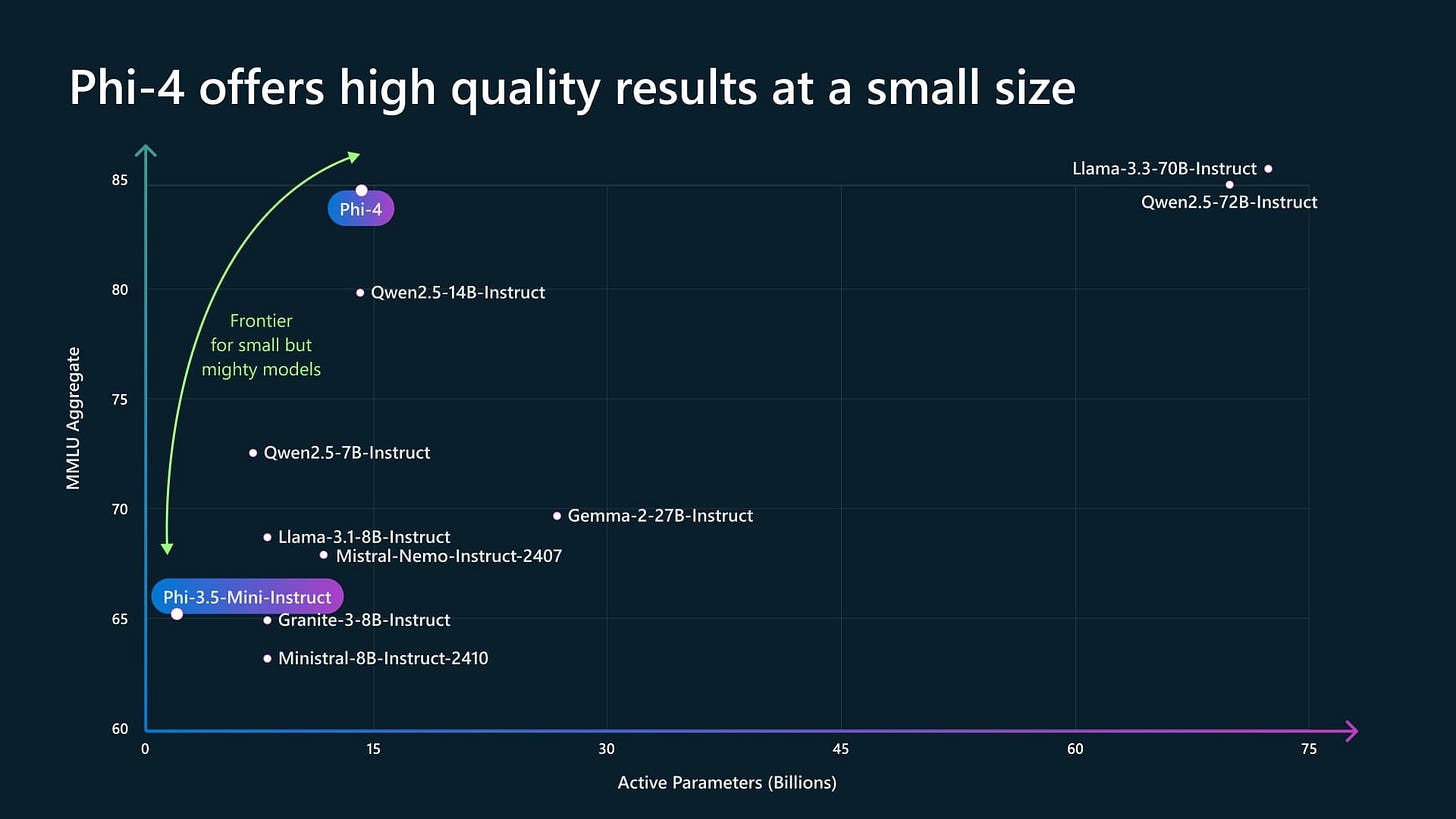
Microsoft's Phi-4: Small Model Packs a Big Punch in Complex Reasoning
Microsoft has released Phi-4, a 14 billion parameter small language model (SLM) that achieves impressive results in complex reasoning, especially in mathematics.
This model notably outperforms much larger models like GPT-4o and Gemini Pro 1.5 on various math and reasoning benchmarks.
Phi-4's training process utilised primarily synthetic data, with AI generating and validating approximately 400 billion tokens of training material.
Additionally, Phi-4 has an upgraded mechanism allowing it to process longer inputs, up to 4,000 tokens, doubling the capacity of its predecessor, Phi-3. This advancement shows that smaller models can achieve high performance.
Why it Matters
Phi-4’s success challenges the common belief that larger models are inherently superior.
By demonstrating comparable or even superior performance in specific areas like mathematical reasoning with a much smaller model, Microsoft is showing that efficient architecture and innovative training methods, such as the use of synthetic data, can be more effective than simply scaling up parameters.
This approach has significant implications for the future of AI, suggesting that powerful AI can be more accessible and less resource-intensive, opening up possibilities for deployment on devices with limited computational power.
This focus on efficiency also has positive environmental implications, reducing the energy consumption associated with training and running large language models.
OpenAI's 12 Days: Two Weeks of AI Progress
OpenAI's "12 Days of OpenAI" event has showcased a range of updates. The first week saw the release of the o1 reasoning model (with 34% fewer errors and 80% benchmark reliability), ChatGPT Pro (a $200/month subscription with a 128k context window), Sora (a text-to-video generator capable of 20-second, 1080p videos), and ChatGPT Canvas (a collaborative document editor).
The second week brought further integrations and enhancements to ChatGPT, including its integration into Apple Intelligence via iOS 18.2, the addition of visual abilities to Advanced Voice Mode, the introduction of Projects for session organisation, and improvements to ChatGPT Search, making it available to all users, enhancing its voice mode, and improving mobile speed.
Why it Matters
OpenAI's updates demonstrate a commitment to advancing AI capabilities across various applications.
The o1 model's improvements enhance reliability for complex tasks, while ChatGPT Pro provides powerful tools for professional users.
Sora's release signifies progress in accessible video generation.
The second week's updates focus on enhancing the user experience and expanding ChatGPT's reach.
These advancements contribute to more powerful, versatile, and accessible AI tools for diverse user needs.
📰 Live blog on the releases by Tech Radar
From Scaling to Superintelligence: A Decade of AI Progress
Ilya Sutskever, former co-founder and chief scientist at OpenAI, delivered a NeurIPS 2024 talk charting AI's progress over the last decade, highlighting the scaling hypothesis—larger datasets and networks equate to better performance—as a key driver.
Early AI focused on replicating rapid human tasks using smaller networks limited by compute. Increased compute led to larger models and datasets, ushering in the era of pre-training.
However, Sutskever argues pre-training's limitations are becoming clear: while compute grows, data is finite, reaching "peak data." This necessitates new approaches, with Sutskever suggesting a move towards agentic AI capable of independent reasoning, leading to potentially unpredictable but more powerful behaviour.
He draws parallels with biological evolution, citing hominids' unique brain-to-body size scaling as an example of possible shifts in AI. Early experiments showed a 3.5x speed up using 8 GPUs and pipelining techniques.
Why it Matters
The end of pre-training signifies a pivotal moment, shifting focus from scaling existing methods to developing more advanced AI architectures.
The rise of reasoning agentic AI has profound implications, creating more autonomous systems capable of tackling complex problems beyond current models.
While exciting, this shift raises crucial questions about control and predictability. As AI becomes more independent, managing its behaviour is paramount. Sutskever's vision of superintelligence emphasises preparing for systems with "radically different qualities."
This encourages research into new methods, ensuring beneficial advanced AI development. The shift to agentic AI will allow for more robust and generalisable models, not limited by current data constraints.
Microsoft's AI Vision: Integrating AI into Everyday Products
Microsoft AI CEO Mustafa Suleyman outlined his vision for AI in a recent interview.
He defines AGI as a system capable of performing well across human-level tasks, emphasising practical applications over the singularity.
Microsoft's strategy focuses on integrating AI into core products like Bing and Copilot, prioritising real-world user feedback.
They employ a "weight class" system to benchmark their models against competitors, focusing on FLOPS for specific use cases.
Why it Matters
Suleyman's pragmatic AGI definition shifts focus to immediate applications. Microsoft's product-centric approach makes AI more accessible and valuable to users.
This approach, contrasting with Google's more research-oriented focus, emphasises the importance of strategic direction in AI development.
By prioritising user needs and real-world feedback, Microsoft aims to create AI solutions that are not only technologically advanced but also deeply integrated into everyday life.
📰 Read the full transcript on The Verge
AI Turns Sound into Sight: Generating Street Views from Audio
Researchers have developed an AI that generates street-view images from audio.
Trained on paired audio-visual data, the AI creates visual representations based solely on sound.
Human evaluations showed 80% accuracy in matching generated images to audio, with the AI effectively capturing proportions, architectural styles, and even lighting conditions.
Why it Matters
This technology demonstrates AI's potential to link audio and visual perception, approximating human sensory experience.
This could improve accessibility for visually impaired individuals and aid in urban planning and environmental studies by visualising the impact of soundscapes.
Unveiling the Secrets: How People Use AI in the Real World
Anthropic has introduced Clio, a system for analysing real-world usage of AI assistants while preserving user privacy.
Clio analyses millions of anonymised conversations, grouping them into topic clusters and hierarchies for researchers to explore usage patterns without accessing sensitive data.
Why it Matters
Clio provides valuable insights into how people actually use AI assistants, allowing developers to better align development with real user needs and improve user experience. Key insights include:
Coding and business applications lead the way as dominant use cases, with web development representing over 10% of interactions, highlighting the professional applications of AI assistants.
AI assistants are used for diverse and surprising unexpected applications, including dream interpretation, soccer analysis, and tabletop gaming assistance, demonstrating the breadth of AI's potential applications.
Usage patterns show significant regional and linguistic variations, with a higher prevalence of economic and social issue chats in non-English conversations, indicating cultural influences on AI usage.
This research has significant implications for improving AI safety and governance by providing empirical data on real-world usage.
AI Can Navigate Without a Map: New Metrics Reveal Flaws in Generative AI's World Models
New research reveals that generative AI often lacks a true understanding of the world, despite impressive performance.
Researchers developed two metrics to assess if AI models have formed accurate "world models." Tests on navigation and game-playing tasks showed that even with high accuracy, models often failed to grasp underlying rules.
When minor changes were introduced, performance drastically decreased, highlighting a reliance on learned patterns over genuine comprehension.
Why it Matters
This study has significant implications for real-world AI applications. While AI excels at pattern recognition, it can fail unexpectedly in dynamic environments.
By focusing on genuine understanding, future AI systems can be more adaptable and reliable. This research emphasises the need to move beyond just predictive accuracy and prioritise a deeper comprehension of the world for more robust AI development.









Love the why it matters. Really helps me stay on top of the impact of ai, not just the tech itself