Deep Research 🔍 LLM Defence 🛡️ Beyond Deepfakes 🎥
PLUS: 🍎 Apple's AI strategy to leverage open-source
👋 Your Weekly Dose of AI.
Each week, I wade through the fire hose of AI noise and distil it into what you actually need to know.
🎵 Don’t feel like reading? Listen to two synthetic podcast hosts talk about it instead.
📰 Latest news
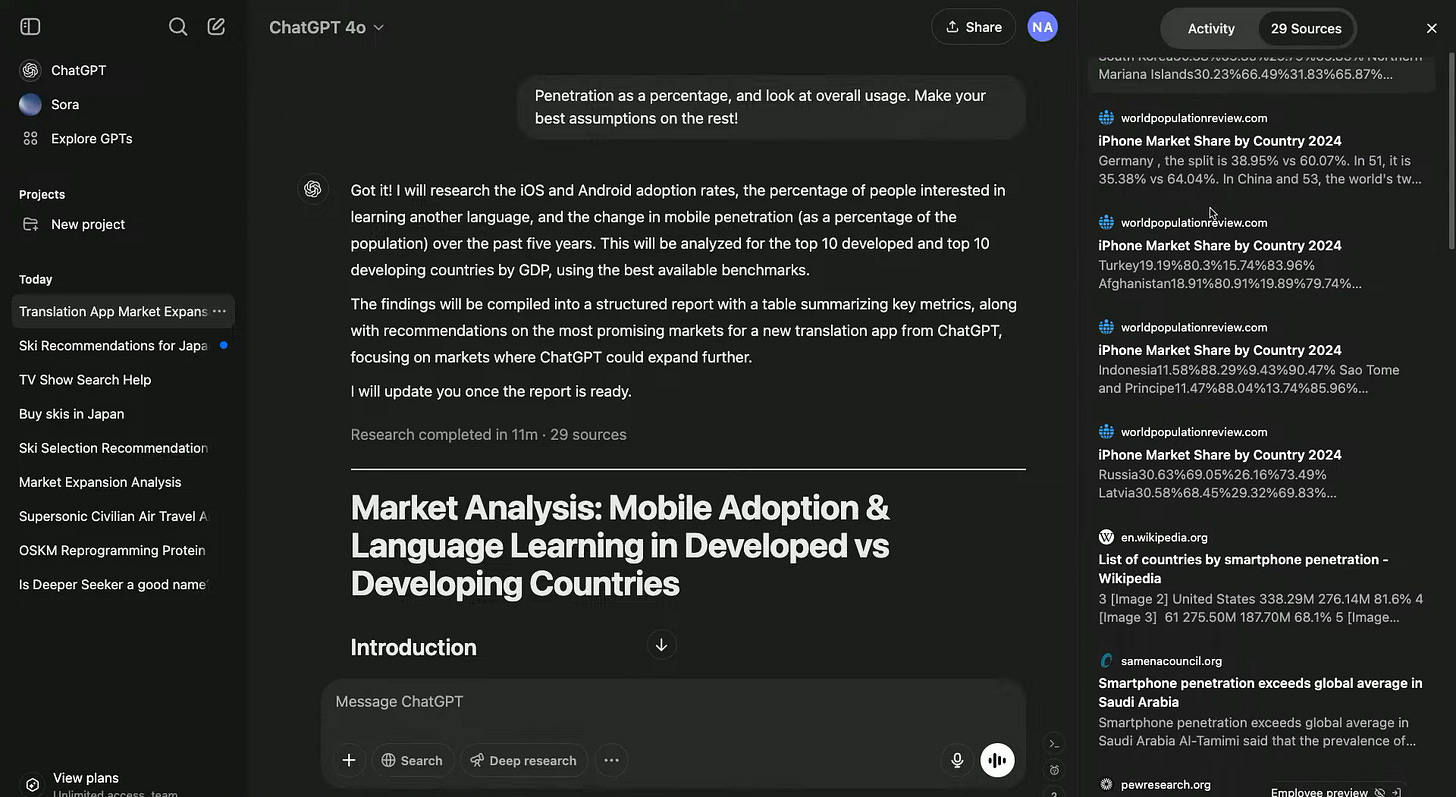
OpenAI's Deep Research: A New AI Agent for In-Depth Online Investigation
OpenAI has introduced "deep research," a new feature within ChatGPT designed to conduct multi-step online research and generate comprehensive reports.
Functioning as an AI research assistant, it aims to streamline in-depth knowledge work across fields like finance, science, and engineering, as well as assist discerning shoppers with research-intensive purchases.
Powered by a version of OpenAI's o3 model (more on this later), deep research leverages reasoning to search, interpret, and analyse online sources including text, images, and PDFs.
The outputs provide detailed summaries of the model's "thinking," alongside citations and source links for verification.
Once again, open-source competitors have emerged just 24 hours after the launch, demonstrating the fast-paced nature of development in this field.
One such project, "open-Deep-Research," a collaborative effort using the Hugging Face platform and OpenAI's o1 model, replicates core functionalities of Deep Research and has already achieved a 55% accuracy rate on the GAIA benchmark.
Currently available to ChatGPT Pro users with a limit of 100 queries per month, access will eventually extend to Plus, Team, and Enterprise users.
OpenAI is developing a faster, more efficient version powered by a smaller model to address cost and access limitations. Deep research is presently accessible via the ChatGPT web interface, with mobile and desktop app integration expected soon.
Why it Matters
Deep research’s ability to automate complex research tasks, hints at how professionals and consumers will gather information in future.
Its agentic nature, performing research independently based on a user's prompt, raises the prospect of replacing time-consuming manual investigation traditionally handled by analysts and consultants.
The model's ability to produce convincingly written reports, complete with citations, has sparked discussion within the AI community about potential over-reliance on AI-generated content without adequate fact-checking.
As highlighted in user feedback on platforms like Hacker News, deep research's outputs, while often impressive, can contain factual errors and hallucinations.
One user reported three distinct factual errors within a 500-word AI-generated report about themselves, underscoring the importance of verifying the information presented.
This concern is further amplified by OpenAI's own acknowledgement of the model's limitations in distinguishing authoritative information and accurately conveying uncertainty.
Despite these limitations, the ability to quickly generate detailed research reports, coupled with access to a wider range of online sources than current models, positions deep research as a potentially powerful tool for information gathering, with many people in the community suggesting that consultancy firms will be impacted as this will replace their services.
The rapid emergence of open-source alternatives further intensifies the competition in this space and suggests that access to advanced AI-powered research capabilities may become more widely available in the near future.
Anthropic's 'Constitutional Classifiers' Defend Against AI Jailbreaks
Anthropic's Safeguards Research Team has introduced "Constitutional Classifiers," a novel method designed to enhance the safety of large language models (LLMs) by protecting them against jailbreaks – adversarial prompts crafted to bypass safety measures and elicit harmful responses.
This technique involves creating a "constitution" of acceptable and unacceptable content categories, then using an LLM (like Claude) to generate synthetic examples of both. These examples, augmented with variations in style and language (including known jailbreak techniques), form a training dataset for input and output classifiers.
These classifiers act as safeguards, filtering potentially harmful content before it reaches the LLM. Initial testing has shown encouraging results.
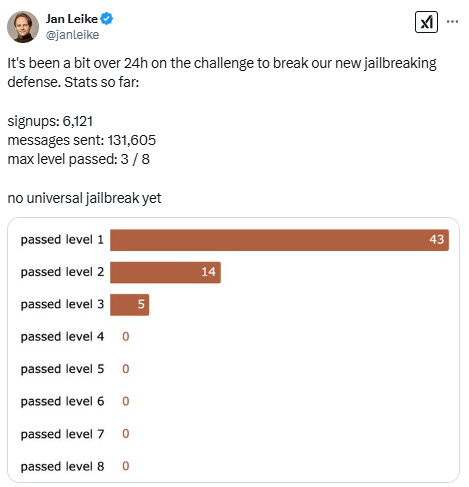
A prototype version withstood over 3,000 hours of human red teaming by 183 participants, with no successful universal jailbreaks (defined as a single jailbreak capable of answering all ten forbidden queries).
Automated evaluations using 10,000 synthetically generated jailbreak prompts demonstrated a reduction in the jailbreak success rate from 86% (baseline) to 4.4% when Claude was guarded by Constitutional Classifiers. This improvement came with a minimal 0.38% increase in over-refusal rates on harmless queries and a moderate 23.7% increase in compute overhead.
A live demo featuring a Constitutional-Classifiers-guarded version of Claude 3.5 Sonnet allows the public to attempt jailbreaking the model. In the first 24 hours of the challenge, over 6,000 people signed up and sent more than 130,000 messages, but no one has successfully bypassed more than three of the eight challenge levels.
Why it Matters
Robust jailbreak defences are vital for safely deploying powerful LLMs. Constitutional Classifiers offer a dynamic approach to mitigating these risks, showing initial success against both human and automated attacks.
The "constitution" can adapt to new techniques, and the public demo provides crucial real-world testing. The challenge's ongoing results will be key indicators of the method's long-term effectiveness.
🎮 Try to jailbreak Claude here
OpenAI’s o3-Mini: A Faster, More Efficient Reasoning Model
OpenAI's new o3-mini is a faster, cheaper reasoning model aimed at STEM, coding, and logic problems.
Coming in three versions (low, medium, and high reasoning effort), it replaces o1-mini, boasting 24% faster responses (7.7 seconds average) and features like function calling and integrated web search with citations.
While lacking vision support (unlike o1), o3-mini-high often matches or bests o1 in benchmarks, outperforming o1-mini across the board.
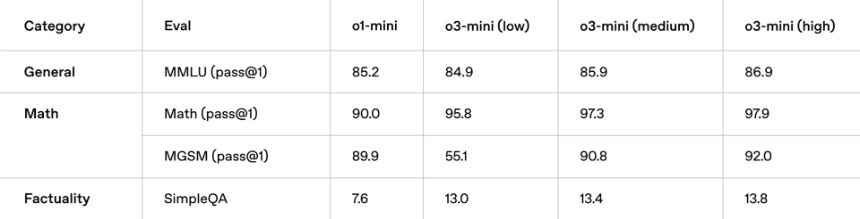
It's available to all ChatGPT users, with expanded access for paid tiers. Though pricier than DeepSeek's R1, it's more competitive than o1. Head-to-head tests against R1 yielded mixed results.
Why it Matters
o3-mini is OpenAI's answer to DeepSeek's R1. Its speed, reasoning prowess, and lower operating costs make it attractive for technical tasks.
Wider availability, including free-tier access to a reasoning model, is a plus. While the absence of vision support is a limitation, o3-mini offers a potent blend of efficiency and performance.
Beyond Deepfakes: OmniHuman and the Coming Flood of AI Content
Watch how the facial movements align with voice - Incredible
ByteDance, the parent company of TikTok, has developed OmniHuman, an AI system that generates highly realistic videos of people.
Unlike previous models, OmniHuman requires only a single image and an audio input to produce videos of varying lengths and styles. The system is remarkably versatile, capable of generating videos with adjustable body proportions and aspect ratios, handling everything from realistic human depictions to cartoon characters and even challenging poses.
This level of fidelity is achieved through a multimodality motion conditioning mixed training strategy, allowing the model to learn from a massive dataset of 19,000 hours of video.
Incredibly realistic Einstein talking about art
OmniHuman also boasts flexible control options, enabling video generation driven by audio alone, video alone, or a combination of both, granting users precise influence over the output.
The quality is showcased through it's ability to render talking, with hand and body gestures, and various singing styles. Crucially, ByteDance has not made OmniHuman publicly available at this time, and they warn against fraudulent offerings.
The hand gestures perfectly align with the voice
Why it Matters
The advancement shown by OmniHuman is that the generated content is now virtually indistinguishable from reality.
Because the system requires only a single image to create these videos, the barrier to entry for generating this type of content is exceptionally low. This suggests that in the near future, numerous applications incorporating this capability will emerge.
It's highly likely that online content will become increasingly dominated by AI-generated material. Consequently, developing new systems for verifying the authenticity of content will be critical, especially for public figures.
The challenge of discerning real from AI-generated content is escalating, and the question of who will become the arbiter of truth in this evolving digital landscape remains unanswered.
📝 Read the paper from ByteDance (many more videos)
Beyond the Hype: Apple's 'Invites' Shows a Different Path for AI
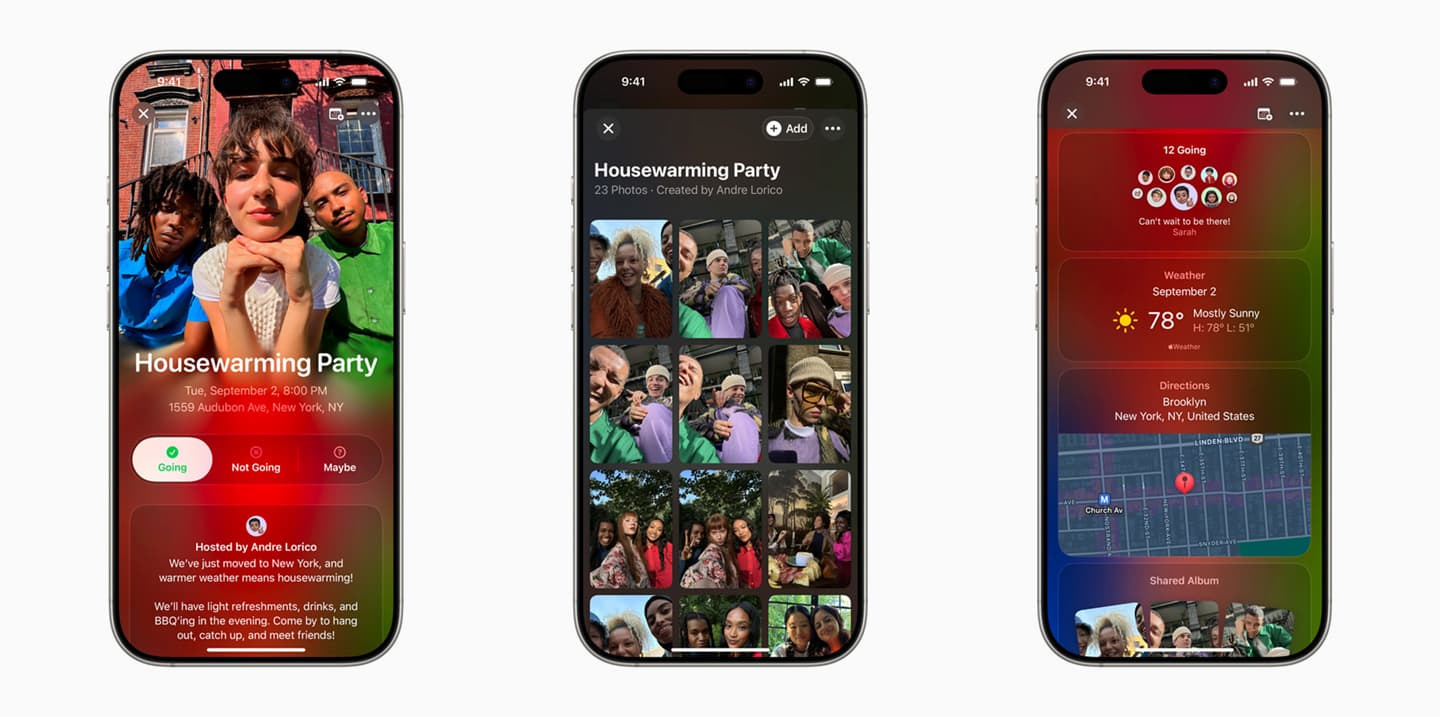
Apple has introduced "Invites," a new event planning app for iPhone that showcases the company's distinctive approach to artificial intelligence.
The app allows users to create custom invitations, incorporating AI-generated images and text through integrations with Image Playground and Apple Intelligence Writing Tools. "Invites" also seamlessly integrates with other Apple services like Photos, Music, Maps, and Weather, providing a unified event management platform.
Notably, while the app is free to download, certain features are tied to iCloud+ subscriptions (starting at $0.99).
Why it Matters
"Invites" is an example of Apple's broader AI strategy, which noticeably diverges from the expensive race to build the largest, most powerful AI models.
While competitors have invested heavily in infrastructure, like the $500 billion "Stargate" project, Apple has decreased its capital expenditures by -13% over the past two years, compared to increases of 73% to 182% for its rivals.
Apple's bet is that AI models will become increasingly commoditised, a trend exemplified by the low-cost, open-source DeepSeek R1 model. The Deepseek example shows open-source models rapidly catching up to closed-source alternatives.
Apple is leveraging this trend by utilising open-source frameworks like AXLearn for its base models, avoiding expensive proprietary systems, and focusing on optimising AI for specific use cases within its ecosystem.
This strategy has, however, faced criticism, with some noting that Apple has lagged behind in AI and that the reception to Apple Intelligence features has been lukewarm, further complicated by delays in their rollout.
Apple's method demonstrates a calculated bet on the future of AI, prioritising user experience and cost-effectiveness over leading the charge in foundational model development.
📝 Invites release post by Apple
📰 Article by the Motley Fool on Apple's AI strategy